The AI Train Is Leaving the Station. Will Your Executive Team Be On It?

As executives, you are responsible for positioning your companies to stay relevant and stay ahead of the technologies that will drive your industries to the next evolution.
One of the most important new technologies within the last few years has been the emergence of AI as a technology poised to change the way many companies do business.
Business leaders are talking about AI in the same way that we talked about the internet in 1995.
Time will tell if these new AI technologies are as business-changing as the other technology revolutions in our lifetimes; many people are sure they will be that – if not even more!
One thing we know is that as executives, we cannot afford to be the last in our category to understand what changes these new technologies bring to the competitive landscape.
This article is just the beginning to give learning-focused executives the fundamental business blocks of the new AI technologies so you can truly lead your teams from the front.
Why Now?
AI has been a subject of research, study, and practical application for decades.
What happened in 2022 changed the business world’s relationship with AI so that today, when we talk about “AI,” we are discussing a whole new paradigm.
ChatGPT 3.5’s launch in November 2022 opened up a new playing field. The significance of the 2022 release was several fold:
- Its well-designed user interface and public-facing data made AI accessible to the general public for the first time. Before ChatGPT 3.5 AI was primarily confined to research labs.
- It revealed the effectiveness of Large Language Models (LLMs), which are the foundation of modern AI.
- It showed impressive abilities to generate human-quality communication, conversations, and language. This natural language capability means it is often called “generative AI”, and is distinguished from other forms of AI.
Without modern LLMs, generative AI would still be primarily in the domain of research labs and universities. So today when we talk about the business uses of “AI,” we usually mean generative AI, LLMs, and the interfaces, tools, & applications that use these technologies.
The Building Blocks of Modern AI
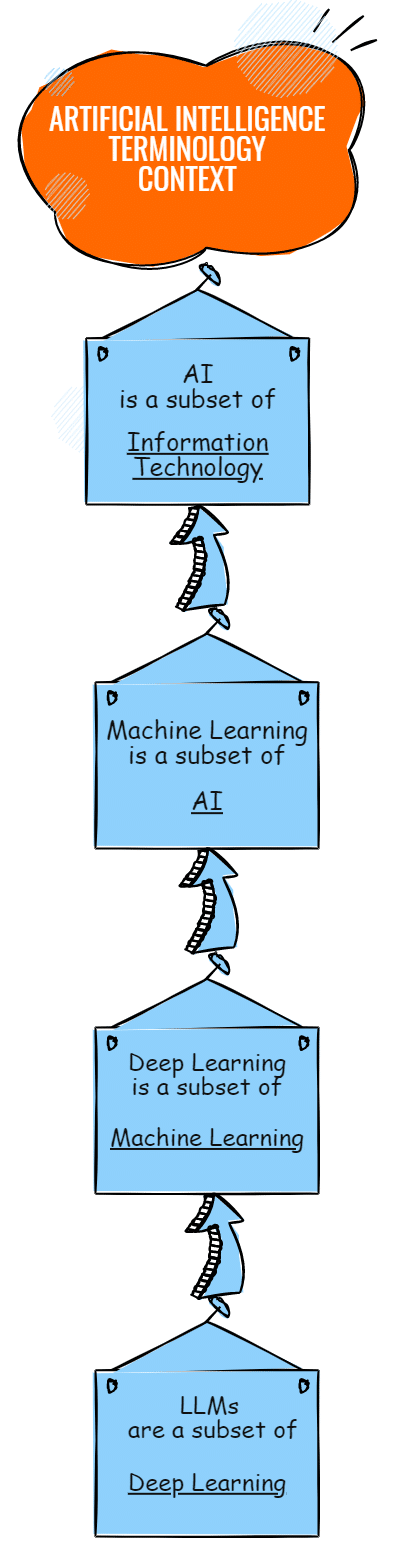
As we discuss artificial intelligence it’s important to be able to understand the common terminology and place them within context to each other. Some of these building blocks are:
- AI
- Machine Learning
- Deep Learning
- LLMs
If we relate these terms as if we were training a new employee:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): This is the big umbrella term. AI is like giving your new employee a brain with the ability to think and make decisions. It’s any system that does stuff we usually consider “smart.”
- Machine Learning (ML): Think of this as the training manual you give your employee. It’s about feeding your AI system lots of data (like past guest reviews or booking patterns) and letting it find patterns on its own. With knowledge of Machine Learning, AI gets better at making predictions
- Deep Learning (DL): This is like installing the training manual into your employees brain. Deep learning is a fancy type of machine learning that manages many layers of information and understands really complex data.
- Large Language Models (LLMs): Think of these like giving your employee the gift of gab. LLMs are particularly good at understanding and generating language, like writing emails, crafting personalized offers, or even being a friendly chatbot on your website to answer questions.
- Tip: When asking ChatGPT to help you understand something about AI, substitute the word “LLM” for “AI”. You will probably get much more helpful results. The term “AI” refers to concepts that include much older and less useful technologies.
Some other terms to know:
Neural Networks: Machine Learning models use neural networks as a building block. Neural Networks are loosely inspired by biological neurons. They consist of layered nodes that transmit signals and adjust connections based on training data.
Generative AI: a type of artificial intelligence that creates new and realistic data, including images, text, or other content, based on patterns learned from existing examples. It does this by using deep learning trained LLMs to give the correct response to natural language questions.
RAG: Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) is a framework that allows for the creation of proprietary Large Language Models (LLMs) to give you a competitive advantage and ensures your business data remains private.
Driving Results With Modern AI
Effective executives adopt AI with a clear understanding of the areas that might provide opportunities for their organization. Here’s how forward-thinking executives might leverage AI for the benefit of their organizations:
- Use AI to help capture and spread knowledge
- Use AI to identify and execute on new opportunities
- Integrate AI into existing processes.
Using AI to help capture and spread knowledge
Effectively capturing and spreading knowledge can be a major challenge in large, complex organizations. AI offers new opportunities to streamline knowledge management and delivery. Artificial intelligence can facilitate the capture of critical insights and expertise as well as optimize access to the right knowledge by the right people. While technology alone isn’t a silver bullet, AI solutions tailored to knowledge management can connect employees to the information they need when they need it. The result is a smarter, more agile workforce positioned to build on existing organizational knowledge rather than constantly reinventing the wheel (or sending too many “can someone point me to. . .?” emails)
- AI facilitates the efficient capture of relevant knowledge by:
- Transcribing: AI can accurately transcribe meetings and discussions, extracting key insights and action items without the need for manual note taking or processing.
- Example: You set Zoom to record your online meeting. Zoom automatically transcribes your Zoom meeting, captures each distinct speaker, and highlights key points and action items (This is a real life example and can be turned on today).
- Asymmetrical Data Mining: AI tools can capture and organize unstructured, asymmetrical data like emails, internal notes, and corporate documents. Relevant knowledge can be identified and organized without manual effort.
- Example: A financial services company uses AI to organize and analyze unstructured data captured during its customer interactions. The AI automatically identifies key customer insights, which is then used to improve the customer experience. This results in increased customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- Build organized knowledge management systems through:
- Relevance Identification: AI can automatically identify and organize the most relevant knowledge from large internal datasets based on usage patterns and connections between content.
- Example: A large healthcare organization uses AI to identify usage patterns and connections between medical literature, patient records, and research findings to identify the most important and relevant information for doctors and nurses in urgent situations.
- Auto Tagging: Documents and media can be automatically tagged with relevant terms to make them more discoverable and referenced more easily across the knowledge base.
- Example: A global manufacturing company uses AI to automatically apply relevant tags to documents, technical manuals, product specifications, and training materials. This allows employees to quickly and easily find the information they need.
- Enabling effective knowledge delivery by:
- Microlearning: Breaking down complex topics into bite-sized on-demand information provided at the moment the employee needs it.
- Example: A customer service representative uses an AI-powered chatbot to quickly resolve a customer’s issue, because the chatbot has been trained on the company’s manuals and can deliver only the relevant information the CSR needs for that customer.
- Individualized Recommendations: Providing personalized recommendations for additional learning based on an employee’s mastery of different topics.
- Example: After taking a skills assessment test an employee will be trained only on the parts of the information they missed on the test.
- Skill Gap Identification: Identifying knowledge gaps across the organization and at the individual level and recommending the domain expert and proper training to address those gaps.
- Example: Employees can be paired to support each other based on how their demonstrated knowledge on a test helps to train the other team member.
Using AI to Innovate and Capitalize on Opportunities
Artificial intelligence opens up exciting new opportunities and business innovation. While AI will not replace human ingenuity, it can significantly accelerate innovation by revealing novel connections and opportunities that even the best analysts could overlook.
Some examples that can help an executive like you better do your job:
Healthcare Industry: AI’s can analyze vast amounts of patient data, including electronic health records, imaging results, and genetic information. This can lead to discovery of patterns and relationships that may lead to new treatments and therapies.
- Example: Discover new drug targets and develop more effective medications, potentially leading to breakthrough treatments for previously incurable diseases.
- An example of this can be seen in this article AI in drug discovery and its clinical relevance
Financial Sector: In the financial sector, AI is disrupting traditional investment strategies and revolutionizing the way financial decisions are made. By analyzing market data, AI can identify trading opportunities that may not be apparent to human traders.
- Example: As one article states, “vast amounts of raw or unstructured/semi-structured data are now promising to provide a new informational edge to investors deploying AI in the implementation of their strategies. AI allows asset managers to digest vast amounts of data from multiple sources and unlock insights from the data to inform their strategies in very short timeframes.”
Anomaly detection: AI can also be used to reduce the time and cost of detecting fraud
- Example: Automated processes can use big data to detect anomalies and patterns in market data, providing insights that can be used to detect fraud. Financial Fraud: A Review of Anomaly Detection Techniques and Recent Advances(p. 22)
Retail Industry: AI is also transforming the retail industry by analyzing customer data to identify trends and preferences. This information can be used to improve product offerings, enhance customer experiences, and optimize marketing campaigns.
- Example: AI can segment consumers in smaller and smaller ways to personalize their recommendations to fit each customer better. Cited:http://dln.jaipuria.ac.in:8080/jspui/bitstream/123456789/14313/1/The-economic-potential-of-generative-ai-the-next-productivity-frontier.pdf (p. 26)
- Monitor customer sentiment on social media and online reviews to identify areas of improvement and address customer concerns.
Other ways AI can lead to new opportunities and innovations
- Generating ideas and hypotheses: LLMs can rapidly synthesize insights from huge datasets and suggest new hypotheses and strategies.
- Improve product design – AI techniques like machine learning and simulation can help companies develop new products faster, customize offerings, and reduce prototyping costs.
- Predict emerging trends – By processing news, social media, market research, and other unstructured data sources, AI can reveal new trends companies can capitalize on ahead of competitors.
- Generative reporting: They can generate reports with key findings and recommendations, saving time and resources for analysts.
- Create new business models – AI makes possible entirely new revenue streams and business models such as intelligent chatbots, hyper-personalized offerings, and data monetization.
- Testing and iterating: They can quickly generate different variations of text content like product descriptions or ad copy for A/B testing, optimizing effectiveness.
In summary, by augmenting human capabilities and revealing insights it would take humans years to uncover, AI can reveal new products, processes, strategies, and even business models. Leveraging these AI capabilities with prudence has the potential to enhance business results and reveal growth opportunities you may be missing today.
Integrating AI Into Existing Processes
AI has the potential to improve our current business processes and work. Done well, AI can transform existing competencies into more efficient and productive engines.
Organizations should begin by auditing current processes to identify the most high-value areas for AI improvement based on measurable metrics.
Already AI has proved itself objectively useful with some very high-profile success stories in the following areas:
Customer Service:
- Chatbots and virtual assistants: Providing 24/7 support, answering common questions, and resolving simple issues, freeing up human agents for complex inquiries.
- Sentiment analysis: Understanding customer feedback, identifying areas for improvement, and personalizing interactions.
Marketing and Sales:
- Personalization: Tailoring marketing campaigns and product recommendations to individual customer preferences and needs.
- Lead scoring and qualification: Identifying promising leads and prioritizing sales efforts.
- Demand forecasting: Predicting future customer demand to optimize inventory and production.
- Content creation: AI can generate content like product descriptions, ad copy, or social media posts to improve efficiency and consistency.
Operations and Supply Chain:
- Fraud detection: Identifying and preventing fraudulent transactions in real-time.
- Inventory Management: This is done by Forecasting supply chain disruptions, optimizing logistics, and improving inventory management.
- Data analysis: Identifying patterns and insights from large datasets that would be impossible to analyze manually.
Risk Management and Compliance:
- Anomaly detection: Identifying unusual activity that could indicate fraud or security breaches.
- Regulatory compliance: Automating compliance checks and reporting.
For true transformation, processes may need a fundamental redesign with AI capabilities in mind. This integration requires cross-functional collaboration between business leaders, AI professionals and employees who manage daily workflows. With strategic integration focused on augmenting human strengths, AI can drive improvements in business performance, efficiency and competitive advantages.
Conclusion
The emergence of AI technologies like large language models represents a strategic inflection point for business leaders across every industry. To leverage AI to its fullest and avoid being left behind, executives must educate themselves on modern techniques, use cases, and implementation considerations.
This starts with gaining an executive view of core AI concepts from machine learning to neural networks. Understanding AI’s possibilities in areas like knowledge management, opportunity creation, and process improvement is crucial. Adopting measurable business-driven approaches focused on augmenting human capabilities is
Executives have an obligation to position their companies for AI success. But they need not become technologists themselves. By combining business acumen, key partnerships, AI fluency and prudent experimentation, leaders can thoughtfully introduce AI to create competitive advantage.
The strategies and concepts covered in this article are designed to equip executives with the mindset and knowledge necessary to evaluate if, when. and how their organizations can benefit from artificial intelligence.
The time for enlightened executives to embrace AI as a way to increase efficiency, insights and differentiation is now. With the right approach, AI can transition from buzzword hype to practical solutions that drive real business results.
Further reading suggestions:
McKinsey & Company The economic potential of generative AI The next productivity frontier
Generative AI: The Insights You Need from Harvard Business Review (paid)